If you are starting your CFA Level 1 journey, one of the first questions you will ask is —
“How many hours do I actually need to prepare?”
You might have seen people on forums quoting numbers like 250 to 300 hours, saying it is enough to clear Level 1.
While that might be true for some, the reality is more layered. The right amount of time truly depends on:
✅ Your background – Are you from finance, accounting, or completely new to these subjects?
✅ Your goals – Are you aiming to simply scrape through or genuinely master the concepts?
✅ Your seriousness & discipline – Are you consistent, or will you squeeze studies only on weekends?
🏗️ The Two Types of CFA Aspirants
🎯 1. The “Just to Pass” Group
This group usually targets 250 to 300 hours.
It works if you already have a strong grasp of financial statements, quant, and economics. Many people with BCom, CA, or finance-heavy MBAs fall into this category.
But be clear — this approach comes with trade-offs.
It means you will focus only on what is needed to get over the line, without truly internalizing the concepts.
And even then, it is not guaranteed. CFA exams are designed to surprise you, especially if your understanding is shallow.
🏆 2. The “Mastery” Group (which I always recommend)
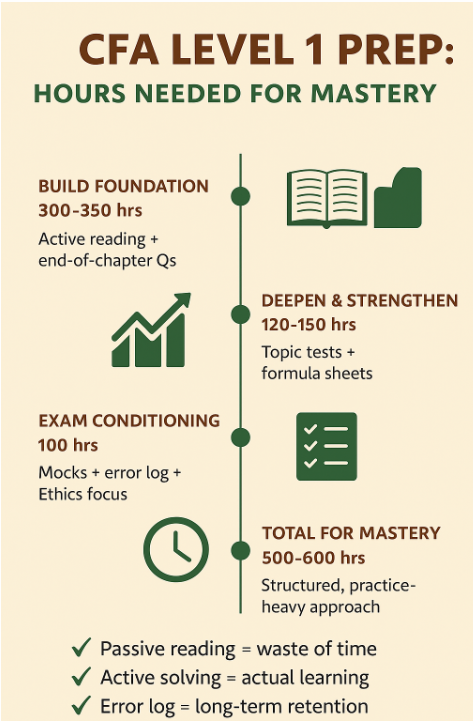
If your goal is to build a solid foundation — not just for Level 1, but also for Level 2, Level 3, and your actual job in investment analysis or portfolio management — then aim for 500 to 600 hours.
Why so much?
Because CFA Level 1 is not just about cramming. It covers ethics, financial reporting, corporate finance, equity, derivatives, alternative investments, portfolio management, fixed income — and expects you to understand how these connect.
A weak base now will haunt you in Level 2, which dives even deeper.
⏳ What Does a Smart Time Plan Look Like?
Here’s a structured timeline that has worked for hundreds of my students:
🗓️ Months 1 to 3 — Build Your Foundation (300–350 hours)
- Read all study material actively, not just to complete pages.
- After each reading, solve the end-of-chapter questions immediately.
- Do topic-wise short quizzes to reinforce concepts.
- Keep a simple error notebook from day one.
- This is the heaviest phase — expect to invest around 25-30 hours a week if you are spreading over three months.
🗓️ Months 4 to 5 — Strengthen & Deepen (120–150 hours)
- Start combining readings. Revise earlier topics along with the newer ones.
- Do more complex problem sets.
- Build formula sheets, practice quick recall.
- Start introducing mini mocks (half tests on multiple topics).
🗓️ Month 6 — Exam Conditioning (100 hours)
- Take at least 3 full mock exams, ideally spaced 10–12 days apart.
- Analyse every wrong answer — was it a conceptual gap, silly mistake, or panic?
- Keep revising ethics regularly. Ethics is notorious for tripping up scores.
🚀 It is Not Just About the Hours
Too many candidates obsess over the total hour count. The truth?
How you use your time matters far more.
- Passive reading means your hours mean little.
- Active practice (solving, reviewing, retesting mistakes) means real learning.
- Keeping an error log means you never repeat the same mistake twice.
💡 Quick Summary
| Goal | Hours Needed | Focus |
| Just to pass | 250–300 hrs | Skim concepts, do basic practice |
| True mastery | 500–600 hrs | Thorough reading + extensive practice + mocks |
🔥 My Last Words
Your CFA charter will stay with you for life. It will open doors and shape your reputation.
So do not cut corners.
Build your foundation now — your future Levels (and your career) will thank you.
If you want, I can even send you a detailed 4- or 5-month plan with weekly targets. Just drop me a message.
✅ Bookmark this page and return to it as you plan your schedule.
Remember, you are not studying just to pass an exam. You are preparing to be a professional who truly understands investments.
NIRAJ AND RAJESH – YAHAAN FAQs BHI RAHEGA – TOH WOH DEKH LIJIYEGA EK BAAR
❓ FAQs: CFA Level 1 Prep Time
How many hours should I ideally study?
➡ For mastery, plan 500–600 hours.
For just scraping through, maybe 250–300, but it is risky.
Can I clear Level 1 with 3 months of prep?
➡ Only if you can give 25–30 hours a week and already have a strong finance background.
Is it okay to skip end-of-chapter questions and only do mocks later?
➡ No. Your foundation is built during readings + topic-wise questions. Mocks only test what you already know.
How many mocks are enough?
➡ At least 3 full mocks under timed conditions.
Analyse each thoroughly.